On this page:
Appendix 1 – Planning scheme style guide (A to Z)
This style guide applies to the VPP and planning schemes and is to be used in conjunction with the Ministerial Direction - The Form and Content of Planning Schemes. The style guide establishes standard style requirements to guide a consistent format for planning schemes.
Acronyms
Acronyms are useful to avoid repeating lengthy expressions. Do not use acronyms in a control. They may sometimes be suitable in a policy where a term is mentioned many times within a policy. If you use an acronym, always spell out the title in full at the first mention, followed by the acronym in brackets.
| ✔ |
First mention: Gumnut Central Activity Centre (GCAC) Subsequent mentions: GCAC |
|---|
A full stop is not required between the letters of an acronym. Plurals of acronyms do not carry apostrophes:
| ✔ | NACs |
|---|---|
| ✖ | NAC’s |
Active or passive voice
(Also refer to Sentence construction, below)
Active voice in statutory writing is better than passive voice because it is more direct and less ambiguous. Active voice places the object after the verb.
| ✔ | Active: Discourage the rezoning of isolated areas of rural land for residential purposes. |
|---|---|
| ✖ | Passive: The rezoning of isolated areas of rural land for residential purposes will generally not be supported. |
| ✔ | Active: Limit the use of court or dead-end street layouts to circumstances where no other option is achievable. |
| ✖ | Passive: The use of court or dead-end street layouts shall be limited to circumstances where no other option is achievable. |
Active voice generally encourages the use of stronger verbs that bring the activity to life. The passive voice can be ambiguous because it submerges responsibility for an action when a more open approach would be clearer and fairer to readers.
And or &
Only use the ampersand symbol (&) in references and tables.
And/or
Do not use ‘and/or’ in statutory writing, it is often ambiguous. In most cases using one or the other conveys the meaning. Otherwise rewrite so that the meaning is clear.
Apostrophes (’)
Apostrophes are used to:
- indicate missing letters
- show possession
When the apostrophe comes before the ‘s’ it indicates singular possession:
| ✔ | The program’s objectives (the objectives of the program) |
|---|
When the apostrophe comes after the ‘s’ it indicates plural possession.
| ✔ | Many rural estates’ common features |
|---|
Brackets (parentheses)
Use parentheses not other forms of bracket. Brackets are used to introduce asides, explanations or additional information and to create emphasis. They are also used to enclose an acronym after a full name:
| ✔ |
The government funded nearly 70 per cent ($7 billion) of welfare expenditure. Most of the company’s employees work part-time (see Table 7). The Department of Transport and Planning (DTP). |
|---|
Capitalisation
Generally, terms associated with government should be capitalised when referring to full, official names and lower case when the name is reduced to the generic element or adjective.
| Victorian Government | the government |
| Department of Planning | the department |
| Gumnut Ranges Steering Committee | the committee |
| Minister for Planning |
the Minister (the Minister is an exception to this rule) |
The terms ‘responsible authority’ and ‘planning authority’ are not capitalised.
The term ‘amendment’ is not capitalised (for an unnumbered mention) but is capitalised when named in full as a proper noun. For example ‘Amendment C31’.
The term ‘council’ is written in lower case, unless referring to the specific name. For example ‘Gumnut City Council’.
Capital ‘S’ is used for ‘state’ when referring to the ‘State of Victoria’ or ‘the State Government’, but lower case in all other instances, including when it is abbreviated to its generic term or used as an adjective.
| ✔ | The State Government will implement the initiative... |
|---|---|
| ✔ | ...if permit conditions can be applied across all planning schemes then they should be included in a state standard provision. |
Contractions
Contractions include shortened forms of words, or two words commonly pronounced as one.
Contractions of two words such as don’t (do not), shouldn’t (should not) and it’s (it is) should be avoided in statutory provisions as they produce a casual tone to the writing.
Commonly understood contractions that are a shortened form of words such as Rd, St or Pty Ltd may be used in planning scheme writing.
Dates
Present dates from the smallest unit to the largest in the order of day, month and year.
| ✔ | 12 April 2018 |
|---|---|
| ✖ | April 12 2018 |
| ✖ | 12th April 2018 |
Dictionaries
The dictionary for planning scheme use is The Macquarie Dictionary.
e.g. and i.e.
Avoid using abbreviated Latin terms in a planning scheme. If necessary, use ‘for example’ or ‘such as’ instead of ‘e.g.’.
Do not use ‘i.e.’ or alternative terms (including ‘that is’ and ‘in other words’) as these terms are too casual for a statutory instrument and a provision should be clear enough that it does not need further elaboration.
Fractions
Spell out fractions except when used in a table or where space is an issue:
| ✔ | three-quarters |
|---|---|
| ✖ | ¾ |
It will usually be better to use a decimal number.
Grammar
Verbs describe an action or a state of being:
| Action | prevent, enable, assist, reduce, limit, facilitate |
|---|---|
| State of being | be, become, exist |
See Appendix 2 for a list of verbs that may be used when writing for the PPF. Choosing verbs deliberately to relay a precise meaning is key to making strong and clear policy.
Take care that your verb choice provides for an achievable outcome through planning. For example, only use a term like ‘ensure’ when the outcome can actually be ensured using the planning system.
The starting verb to a PPF strategy also needs to be followed with meaningful content to make a policy clear. Open-ended verbs like ‘improve’ often need more explaining (for example, to set out what is considered an improvement).
Nouns provide names for people, places or things as well as abstract notions.
- Common nouns name any generic person, place, thing or idea. They are not capitalised unless they come at the beginning of a sentence.
- Proper nouns are the names of specific people, places, things or ideas. Proper nouns should always be capitalised.
| Common Noun | Proper Noun |
|---|---|
|
|
Pronouns stand in for a noun or noun phrase already mentioned in a text.
| he, she, it, they |
Adjectives modify (describe, define or evaluate) a noun or pronoun. Avoid using emotive adjectives and ensure any unclear adjectives are substantiated. For example, by explaining what comprises an ‘attractive’ space where this is sought in policy.
| attractive, tall, functional, safe, compact, convenient |
Headings
Refer to the style sheet in the Ministerial Direction The Form and Content of Planning Schemes for the correct styles to use.
Inverse statements
Consistent with avoiding repeated content in provisions, avoid restating a provision using inversed wording. The repetition does not make the provision stronger.
| ✖ |
Gaming machines should only be located in neighbourhoods with a low concentration of gaming machines. Gaming machines should not be located in neighbourhoods with a high concentration of gaming machines. |
|---|
| ✖ |
Discourage dwellings that are not associated with the agricultural use of the land. Support dwellings only where they are associated with the agricultural use of the land. |
|---|
Jargon
Use professional language. Do not use emotive terms, colloquialisms or popular speech in statutory writing.
Keep language simple and professional and avoid casual or popular conversational language or terms that are uncertain. For example, where a policy seeks to make a place ‘colourful’, ‘exciting’, ‘vibrant’, ‘cosmopolitan’ or ‘green’, or where you may seek ‘statement’ design. Using abstract terms makes your message ambiguous.
Avoid using colloquial terms, including planning dialect such as ‘permit trigger’ and ‘as-of-right’, so that new or infrequent system users, or less-experienced professionals are not alienated or confused by unknown terms.
| ✖ | ‘as-of-right' |
|---|---|
| ✔ | ‘No permit required’ |
Latin and words from other languages
Do not use words from languages other than English:
| Ultra vires, pro forma |
Use a plain English term instead. If such a word must be used, use italics and ensure the meaning is clear.
Measurements
Always spell measurements in full in the body of your text. Only use abbreviations in tables and graphs:
| Measurement | Abbreviation |
|---|---|
| hectare | ha |
| metre | m |
| kilogram | kg |
| millimetre | mm |
Symbols for units of measurement do not use full stops and are never plural:
| 43.5 ha and 20 kg |
Include a space between the number and the unit of measurement.
Use numerals for measurement when they are accompanied by a symbol. Also use numerals in mathematical contexts (such as equations and ratios) and in tables:
| 3 km, 9°C, $3.50, 2+2=4 |
Numbers
Write numbers less than 10 in full, except for:
| exact measurement: | 5 inches, 3 per cent |
|---|---|
| a series of quantities: | 2, 4, 6 then 8 groups followed |
| numbers of millions or billions: | $12 million |
Numbers from 10 and above should be expressed numerically.
Never start the beginning of a sentence with a number. If this is unavoidable, spell out the number, even if it is 10 or greater.
Use commas in numbers of four digits and above.
| ✔ | 4,000 |
|---|---|
| ✖ | 4000 |
In spans of numbers use a dash with no space before or after. Drop the unnecessary digits in the last part unless it makes the meaning unclear:
| ✔ | 2012–16, 23–9 |
|---|
Per cent
The per cent symbol ‘%’ may be used instead of the term ‘per cent’, particularly in tables or graphs where space is limited. Use ‘per cent’ if it follows a number written as text.
It is per cent (two words).
Place names
For the spelling of Australian place names refer to the Gazetteer of Australia Place Name Search – Geoscience Australia.
Place names should be capitalised:
| ✔ | the Yarra Valley, the Grampians |
|---|
Regions should be capitalised and may contain a hyphen:
| ✔ | South-West Victoria, Central Victoria |
|---|
Use capitals for official or abbreviated titles that remain specific but not for generic references:
| ✔ | The Australian Capital Territory includes Jervis Bay. The territory’s total area is more than 2,000 square kilometres. |
|---|
Apostrophes are not used in Australian place names:
| ✔ | Fishermans Bend, Wilsons Promontory, Halls Gap |
|---|
Positive language
A reader is more likely to accept and remember a point if it is made in the positive.
When the action suggested is clear and the language is uncluttered it is easier to find the meaning:
| ✔ | Positive: Support use and development for a dwelling if a reticulated water supply is available. |
|---|---|
| ✖ | Negative: Use and development for a dwelling will not be permitted where a reticulated water supply is not available. |
Slashes (/)
Do not use slashes in statutory writing. Write 'or' instead of a slash.
Spelling
Use Australian English or British English spelling, rather than American English.
| Australian English | American English |
|---|---|
| ✔ characterised ✔ metre ✔ colour ✔ centre | ✖ characterized ✖ meter ✖ color ✖ center |
Make sure that the spell-check on your computer is set to Australian English. To adjust the settings in MS Word, select Review > Language, then choose English (Australian).
Your spell check should not be your sole means of proofreading. Always check copy yourself. While spell checkers will pick up spelling mistakes, they may not pick up words that have been misused or left out of sentences.
Use The Macquarie Dictionary as your reference.
Tautology
Tautology refers to repetitive, unnecessary words or phrases that say the same (or similar) thing twice consecutively. Removing tautology delivers more direct and concise writing.
| Examples to avoid | |
|---|---|
|
✖ close proximity ✖ grow and expand ✖ protect and conserve ✖ currently undergoing ✖ integral part |
✖ enhance and improve ✖ support and promote ✖ image and character ✖ facilities and services ✖ including but not limited to |
There are, however, instances where ‘double-barrelled’ references may be needed. For example, ‘protect and enhance’ are terms often used together when addressing heritage. These terms each have a different effect and if both are intended, they may be mentioned together.
That and which
Use ‘that’ to introduce restrictive information. ‘That’ tells you a necessary piece of information about its antecedent.
‘Which' is non-restrictive: it does not limit the phrase it refers to, but simply provides an extra piece of information about something being discussed.
As a rule of thumb, if a phrase following ‘which’ or ‘that’ can be removed without changing the meaning of a sentence, ‘which’ can be used. If not, the term ‘that’ should be used. The examples below demonstrate how the use of ‘which’ or ‘that’ may change the effect of a policy.
| ✖ | Discourage signs which obscure major view lines. |
|---|---|
| ✔ | Discourage signs that obscure major view lines. |
In the example above, the intent is to discourage only those signs having the effect of obscuring major view lines, not all signs.
| ✖ | Support infill residential development in the General Residential Zone which respects the neighbourhood character of the area. |
|---|---|
| ✔ | Support infill residential development in the General Residential Zone that respects the neighbourhood character of the area. |
In the example above, the intent is to support only infill development that respects the neighbourhood character of the area, not all infill residential development. The latter part of the sentence is intended to define the type of infill development that is acceptable; it is not intended as added context or to be read as a digression.
Time
The abbreviations ‘am’ and ‘pm’ do not have full stops. A full stop should be used to separate the hours from the minutes:
| ✔ | 9.15 am |
|---|
Drop the extra zeros for hours.
| ✔ | 10 am |
|---|---|
| ✖ | 10.00 am |
Web addresses
Italicise names of websites if they are not written in full. Bold URLs that are written in full. Underline them only if they are live links.
Web addresses do not require ‘http://’ to be included at the start.
Appendix 2 – Planning Policy Framework verbs
The list below suggests verbs to use and those to avoid when writing strategies for the PPF. A verb is not automatically suitable because it is included in this list. Verbs must be chosen carefully to achieve the intended outcome.
Encouraging verbs
- Allow: to grant permission to or for
- Assist: to give support, help or aid
- Enable: to make possible or easy
- Enhance: to raise to a higher degree, intensify or magnify
- Encourage: tostimulate by assistance; approval
- Facilitate: to make easier or less difficult
- Improve: to bring into a more desirable or excellent condition
- Promote: to further the growth, development, progress of; encourage
- Prioritise: to give priority to
- Strengthen: to make stronger
- Support: to uphold by aid; advocacy or endorsement
- Upgrade: to assign to a higher status; to improve
Protective verbs
- Conserve: to keep in a safe or sound state; preserve from loss, decay, waste or injury
- Maintain: to keep in existence or continuance; preserve; retain; to keep in due condition, operation or force.
- Preserve: to keep alive or in existence; make lasting; to keep safe from harm or injury
- Protect: to cover or shield from injury or danger
- Respect: to treat with consideration; relate or have reference to
- Retain: to keep possession of; to continue to use, practise; to hold in place or position
Conclusive verbs
- Avoid: keep away from or keep clear of
- Ensure: tomake sure or certain to occur
- Prevent: to keep from occurring; hinder
Discouraging verbs
- Limit: to confine or keep within limits; to restrict
- Minimise: to reduce to the smallest possible amount or degree
- Reduce: to bring down to a smaller extent, size, amount; to lower in degree, intensity
- Restrict: to confine or keep within limits as of space, action, choice or quantity
- Discourage: to express disapproval of; to dissuade from; to obstruct by opposition
Neutral verbs
(could encourage or discourage depending on context)
- Accommodate: to find or provide space for (something); to make suitable or consistent
- Allocate: to set apart for a particular purpose; assign or allot
- Concentrate: to bring or draw to a common centre or point of union; cause to come close together
- Connect: to join or unite; link
- Consolidate: to unite or combine; to strengthen
- Coordinate: to place or arrange in due order or proper relative position; to combine in harmonious relation or action
- Create: to bring into being; cause to exist; produce.
- Define: to determine or fix the boundaries or extent of; to make clear the outline or form of; to explain the nature or essential qualities of
- Deliver: to give forth or produce
- Demonstrate: to make evident by arguments or reasoning; prove
- Design: a plan to be executed or constructed; a plan; a project; a scheme
- Develop: to bring to a more advanced or effective state; to cause to grow or expand
- Direct: to regulate the course of; conduct; manage; control; to point or aim towards a place or an object
- Establish: to set up or bring about; to settle or install in a position
- Focus: (to make) a central point of attraction, attention or activity; to concentrate
- Implement: to put (a plan, proposal etc.) into effect
- Increase: to make greater in any respect; augment; add to
- Locate: to set, fix or establish in a place, situation or locality
- Manage: to take charge or care of; to handle, direct, govern or control in action or use
- Offset: to balance by something else as an equivalent; to compensate for
- Plan: a scheme of action or procedure; a design or scheme or arrangement
- Provide: to furnish or supply
- Reinforce: to strengthen; make more forcible or effective
- Reserve: to keep back or save for future use, disposal, treatment; to retain or secure by express stipulation
- Restore: to bring back to a former, original or normal condition
- Specify: to mention or name specifically or definitively; to give a specific character to
- Transition: to move from one state, position or stage to another
- Undertake: to warrant or guarantee; to take in charge
Verbs to avoid
(provide little/no direction)
- Consider: to think carefully; to view attentively or scrutinise
- Recognise: to perceive as existing or true; to acknowledge formally as existing
- Acknowledge: to admit to be real or true; to indicate appreciation or gratitude for; to certify the receipt of
(controls cannot be included in policy)
- Require: to place under an obligation or necessity
02 Municipal Planning Strategy
02.01 Context
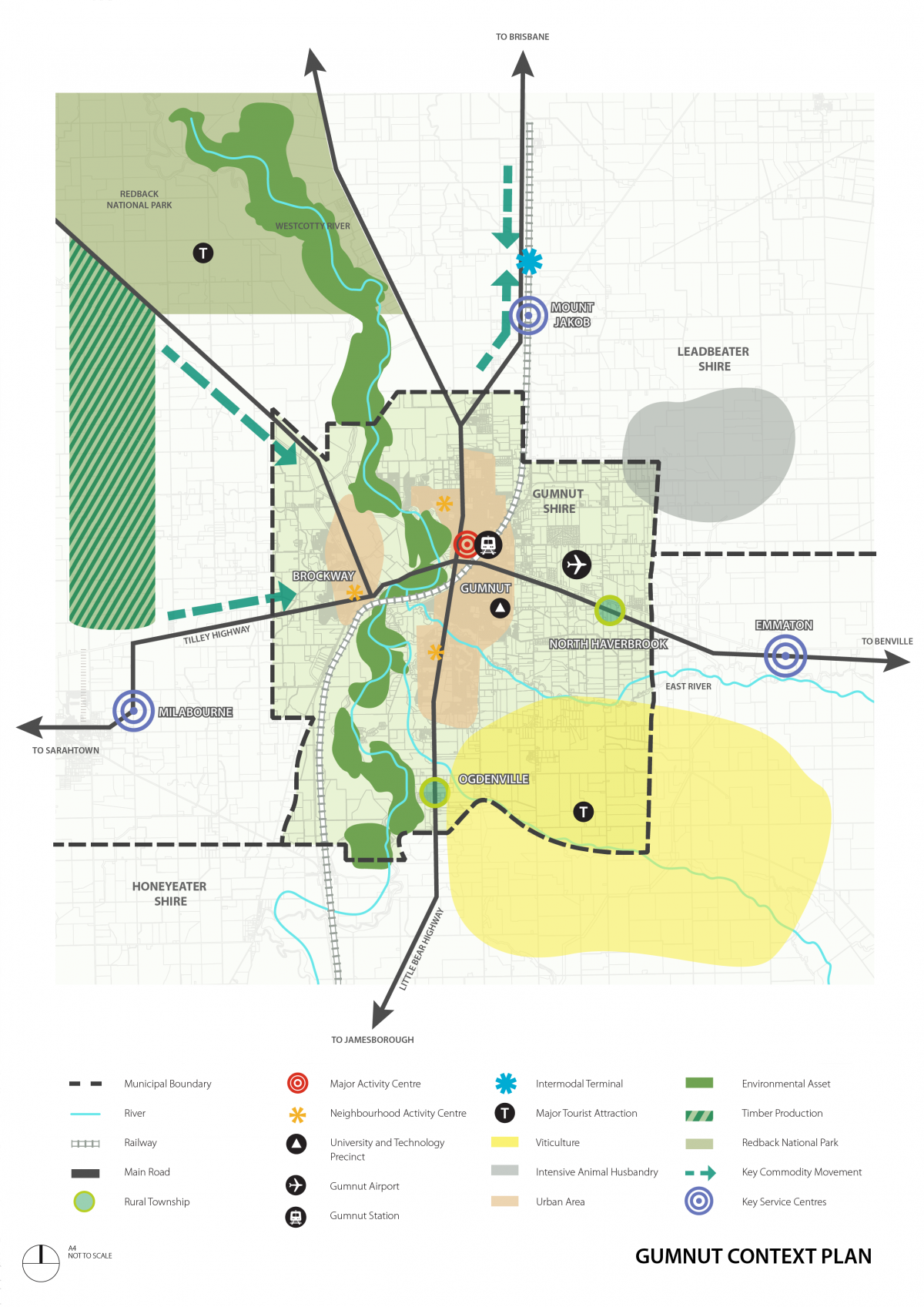
Gumnut Shire is about 250 kilometres north-west of metropolitan Melbourne. It has an urban core, surrounding rural townships and a large agricultural base across approximately 170 square kilometres. The Gumnut City Town Centre is a major activity centre on the state’s northern transport corridor.
There are shared boundaries, connections and relationships with Leadbeater Shire to the north and Honeyeater Shire to the south.
The population of about 70,000 in 2016 is forecast to grow to about 100,000 by 2040, making Gumnut Shire one of Victoria’s fastest growing regional municipalities.
Gumnut Shire’s catchment extends beyond its borders and includes major retail, health and education facilities. People are attracted to Gumnut for its character and lifestyle as well as its employment and education opportunities.
Gumnut’s most important natural feature is the Westcotty River, a major tributary of the Murray River. The river environs include substantial areas of high-value biodiversity. The river and its surrounds make up a substantial portion of the western part of the Shire.
Gumnut Shire has a number of highly significant heritage buildings, structures, features, precincts, archaeological sites, cultural landscapes, trees, avenues and natural features. Gumnut’s natural heritage was formed over 500 million years ago, while its rich cultural heritage began over 40,000 years ago. Much of the remaining pre-contact heritage is concentrated in the area surrounding the Westcotty River.
The agricultural areas of Gumnut Shire are some of Victoria’s richest. Local farming activities deliver some of the highest value production per hectare in the state. Agriculture is also important to the shire’s rural character and identity and is a key driver for tourism in the shire. The popularity of the ‘farm to table’ movement has drawn people to Gumnut Shire because of its strong food and wine-based tourism industry. Service industries, including professional services, education, health, retail, cultural and government are all represented in Gumnut and have been growing strongly over the past decade.
02.02 Vision
Gumnut Shire’s Vision, derived from the Gumnut Shire Council Plan 2017, is to create a place that:
- Fosters economic prosperity by supporting our local businesses and industries and creates an environment in which they can thrive by:
- Supporting agricultural, knowledge industry, tourism, service and industrial uses in the Shire.
- Supporting and protecting the road, air and rail links to the region and the state.
- Is vibrant and sustainable, that we love to live and work in and has excellent connections, facilities and services by:
- Protecting the existing rural character while also providing an attractive and liveable built environment in those parts of the Shire where development will intensify.
- Creating an ecologically sustainable Shire.
- Providing housing to accommodate the expected population growth.
- Achieving a diversity of housing choices, housing affordability and a good standard of building design and amenity.
- Promotes our valued natural and built assets by:
- Managing development so that it is responsive to the existing natural and built environment.
- Safeguarding our valued environmental assets to ensure the health of ecological systems and the biodiversity they support.
- Protecting, conserving and enhancing the Shire’s heritage resources.
02.03 Strategic directions
Settlement
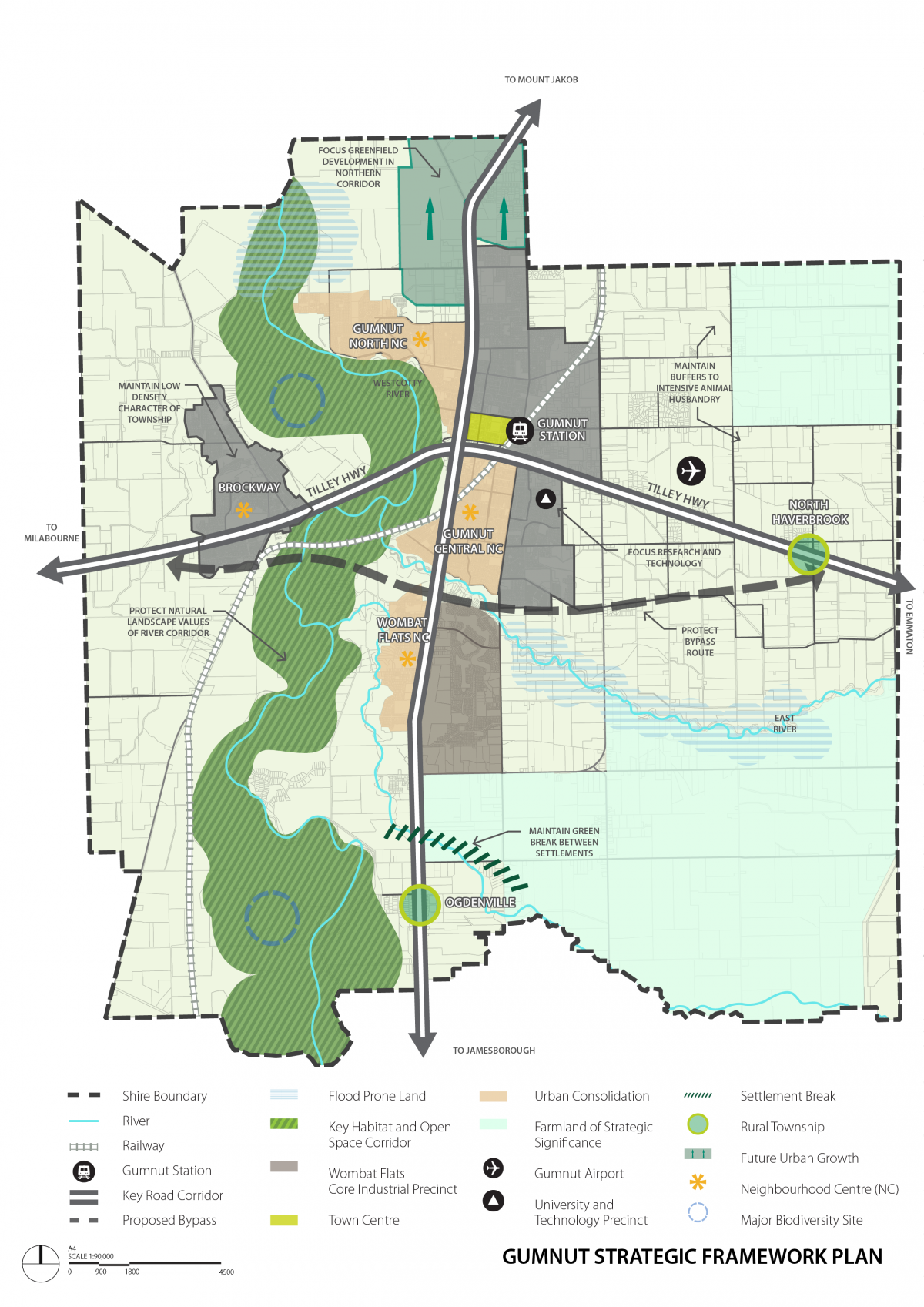
Growth in Gumnut Shire is to be accommodated by consolidating existing urban form, expanding identified towns and providing greenfield development opportunities.
The Gumnut City Northern Growth Area is the primary greenfield development area. Urban consolidation is encouraged in and around Gumnut City’s three neighbourhood activity centres.
The townships of Brockway, Odgenville and North Haverbrook and their surrounding communities provide an attractive lifestyle choice in a rural setting. They represent a different style of living to the more urban form of Gumnut City.
The Gumnut Townships Development Plan 2010 sets out the preferred form for future development in Brockway, Ogdenville and North Haverbrook. While Ogdenville and North Haverbrook are identified for growth, residential development in Brockway will be limited to areas that are already zoned for residential use, recognising the constraints of native vegetation, landscape and heritage character.
Most of the population increase in Gumnut to 2040 is to be accommodated by directing growth to:
- Gumnut City Northern Growth area.
- Urban consolidation areas (including the Wombat Flats, Gumnut Central and Gumnut City North neighbourhood centres).
- The townships of Odgenville and North Haverbrook.
Activity centres
There is a strong network of activity centres providing shopping, employment, entertainment, social and community focal points throughout the Shire.
The Gumnut Shire activity centre hierarchy establishes the order (with respect to scale and function) of one centre compared to another. The spatial distribution and hierarchy of activity centres across Gumnut is shown on the Strategic Framework Plan.
The role and function of activity centres will be supported by:
- Reinforcing the primacy of the Gumnut City Town Centre as a key entertainment destination, service, industry and employment area and inner city living precinct.
- Encouraging uses that provide localised employment and service needs in the Wombat Flats, Gumnut Central and Gumnut City North Neighbourhood Centres.
Natural Environment
Much of the native vegetation that existed in the Shire before settlement has been removed or substantially modified. As a result remnant vegetation, particularly along the Westcotty River, serves an important role in preserving biodiversity, providing habitat and environmental benefits such as water quality control, ground water management and soil stabilisation. The urban break between Ogdenville and Gumnut City is significant in providing the one substantial east-west biodiversity corridor through the municipality.
The Shire seeks to protect biodiversity by:
- Retaining remnant vegetation throughout the municipality but particularly along the Westcotty River.
- Maintaining the urban break between Ogdenville and Gumnut City.
Amenity
Gumnut City’s residential areas are highly desirable due to their access to retail, entertainment, employment, community and recreational facilities. Many of these areas are also aesthetically significant with intact streetscapes. The Shire seeks to maintain residential amenity by:
- Directing non-residential uses to locate in either the Gumnut City town centre or the Wombat Flats, Gumnut Central and Gumnut City North neighbourhood centres.
- Supporting limited non-residential uses in residential areas, provided they serve a direct local need and minimise impacts on the amenity of an area.
- Directing industrial uses, particularly those with adverse amenity impact potential, to the Wombat Flats industrial precinct.
Agriculture
Agriculture is an important economic asset for the Shire and needs to be protected from encroaching, non-compatible uses. In particular, the subdivision or use of land in farming areas for dwellings is discouraged as this has the potential to remove productive agricultural land from supply and create land use conflicts with nearby farming properties.
Agriculture in the Shire will be protected by:
- Supporting the subdivision of land for or construction of a dwelling in the Farming Zone only where it can be demonstrated that the dwelling is reasonably required to support agricultural activity.
Built environment and heritage
Gumnut Shire contains many diverse urban and environmental features identified for preservation and enhancement in order to retain the character of the municipality.
Brockway township was one of the first post-contact settlements in the region and has an extensive and highly intact built heritage.
Vegetation throughout the Shire also provides scenic qualities and contributes to amenity and character.
Gumnut’s activity centres are a key element in promoting activity and social interaction with built form providing the physical basis for this.
Owing to its high-profile location at the southern entry point to Gumnut City, the Wombat Flats industrial precinct forms the primary gateway location for the urban areas of Gumnut.
The Shire will protect its distinctive built and natural environment by:
- Designing built form in activity centres to encourage interaction with the public realm and prioritise pedestrian amenity.
- Protecting, conserving and enhancing its heritage assets.
- Designing infill housing development in existing residential areas to respect existing neighbourhood character.
- Encouraging the retention of existing canopy trees.
- Supporting innovative and contemporary designs for housing in urban consolidation and greenfield development areas that complement the important natural, cultural and historic built form and landscape values of the Shire.
- Encouraging development in the Wombat Flats industrial precinct to achieve a high standard of urban design in order to:
- Create a gateway entry.
- Create a strong sense of place.
- Complement the abutting Wombat Flats neighbourhood centre.
- Provide a quality environment for workers and visitors.
Sustainability
Building design and the pattern of land use and development can contribute substantially to the overall sustainability of the Shire. Lowering the ecological footprint of new housing (and other development) is necessary to accommodate new residents and businesses while minimising impacts on the environment.
Sustainability in the Shire will be supported by:
- Encouraging subdivisions and development in greenfield areas to create a compact form and include facilities that promote sustainable modes of transport.
- Encouraging development throughout the Shire to incorporate environmentally sustainable design principles to reduce its ecological footprint.
Housing
Housing demand is high in Gumnut Shire due to the increasing number of new residents. The supply of housing being developed in Gumnut Shire is not matching the needs of a diverse population, particularly in relation to smaller households, the elderly and disabled persons.
The Shire seeks to accommodate housing demand by:
- Directing more compact dwellings, including apartments and townhouses, to locate in the Gumnut North, Gumnut Central and Wombat Flats neighbourhood centres where urban consolidation is encouraged.
- Supporting the provision of lower cost accommodation, social housing and housing for people of all abilities around the Gumnut City town centre and the three neighbourhood centres.
Economic development
Gumnut Shire has a diverse local economy that is distributed across the primary, secondary and tertiary economic sectors. While agriculture remains a mainstay of the local economy, the Gumnut Airport and Brown Snake University (with its research and technology precinct) are significant economic contributors to both the Shire and the surrounding region. The Shire also has a role in transporting and processing timber from plantations in neighbouring municipalities.
The Wombat Flats industrial precinct is the main manufacturing centre for the Shire. The precinct has a focus on food manufacturing that responds to the high quality and availability of local produce. Businesses in the precinct are a major source of employment for the Shire.
Economic growth in the Shire will be supported by:
- Protecting the Brown Snake University and Technology Precinct from encroaching residential uses, other than where such uses will support the function of the precinct.
- Discouraging uses in or directly adjacent to the Wombat Flats Industrial precinct that are incompatible or would inhibit its function.
- Encouraging tourism uses that support and enhance local agriculture, particularly where they support the viability of smaller farms.
Transport
Gumnut Airport is a valuable asset for the Shire and the region. The airport links the Shire to Melbourne, other state capitals and regional centres. The railway line and Tilley Highway provide important transport links for moving both people and freight. Gumnut Railway Station is a key internodal terminal for the region.
The planned highway bypass will improve the amenity of Gumnut City by removing through traffic. The bypass will also increase the viability of transport links in the area by reducing the time taken to travel through Gumnut City.
As important assets for the Shire and the surrounding region, the Gumnut Airport & Tilley Highway bypass will be protected by:
- Maintaining and growing the recreational, emergency and charter use of the airport.
- Preventing the encroachment of land uses and forms of development that could restrict the future use of the airport or the function of the highway.
02.04 Strategic framework plan
Checklist for including policy in clause 11.03 (Planning for Places)
| 1. Does the proposed policy apply to a specific place? For example ‘Gumnut irrigation district’, not ‘Townships in the City of Gumnut’ which are a type of place, rather than a place. | ☐ |
| 2. Is there a common objective or common set of objectives for the place? | ☐ |
| 3. Does the proposed policy provide guidance specific to the place? Generic content applied loosely to multiple places or precincts in one or more policies should be consolidated and positioned elsewhere in the PPF. | ☐ |
4. Does the proposed policy include content relating to multiple, interrelated issues? Where there are interdependencies between multiple strategies a place-based policy may provide a more coherent strategic narrative. | ☐ |
5. Does the proposed policy result in a clearer and simpler representation of the policy than if it were thematically distributed across the PPF? | ☐ |
| 6. Do the proposed strategies provide detailed policy directions for the particular place? High level strategic directions belong in the Municipal Planning Strategy. | ☐ |
7. Does the proposed policy exclusively comprise content for the place that is not already contained in a control? Policy should not duplicate content in a control that applies to the place, such as a Design and Development Overlay. | ☐ |
The following table provides an overview of the content of state (or regional) policy and indicates where particular local policies should be placed under the various Planning Policy Framework clauses.
This table is intended as a guide only. Correct placement of policy is dependent on a detailed understanding of state and regional policies and local policy content.
Where a state policy relates to a single, well-defined topic (for example planning for ports), no further instruction has been provided as it is considered self-explanatory.
| Clause | PPF heading | Policy content |
|---|---|---|
| 11 | SETTLEMENT | |
| 11.01 | Victoria | |
| 11.01-1 | Settlement |
|
| 11.02 | Managing growth | |
| 11.02-1 | Supply of urban land | The provision of land (residential, commercial, industrial etc.) and infrastructure to support development and meet forecast demand. |
| 11.02-2 | Structure planning | Precinct Structure Plans for growth areas. |
| 11.02-3 | Sequencing of development | Managing development in growth areas so services are available early for new communities. |
| 11.03 | Planning for places | |
| 11.03-1 | Activity centres |
|
| 11.03-2 | Growth areas |
|
| 11.03-3 | Peri-urban areas |
|
| 11.03-4 | Coastal settlement | Planning for sustainable coastal development through:
|
| 11.03-5 | Distinctive areas and landscapes |
|
| 11.03-6 | Regional and local places | Place-based policies that relate to a place that is not covered by clauses 11.01, 11.02 or 11.03-1 to 11.03-5 – such as a township, an urban renewal precinct or a strategic redevelopment area. This clause can only be used for policies that meet all of the criteria outlined in the Place-based policy checklist. |
| 12 | ENVIRONMENTAL AND LANDSCAPE VALUES | |
| 12.01 | Biodiversity | |
| 12.01-1 | Protection of biodiversity |
|
| 12.01-2 | Native vegetation management |
|
| 12.02 | Marine and coastal environment | |
| 12.02-1 | Protection of the marine and coastal environment |
|
| 12.02-2 | Marine and coastal Crown land | |
| 12.03 | Water bodies and wetlands | |
| 12.03-1 | River corridors, waterways, lakes and wetlands |
|
| 12.04 | Alpine areas | |
| 12.04-1 | Sustainable development in alpine areas | |
| 12.05 | Significant environments and landscapes | |
| 12.05-1 | Environmentally sensitive areas | Protection of environmentally sensitive areas with significant recreational value. |
| 12.05-2 | Landscapes | Significant landscapes and open spaces that are not distinctive landscapes identified at Clause 11.03-5. |
| 13 | ENVIRONMENTAL RISKS AND AMENITY | |
| 13.01 | Climate change impacts | |
| 13.01-1 | Natural hazards and climate change |
|
| 13.01-2 | Coastal inundation and erosion | Coastal impacts of climate change. River and coastal development susceptible to inundation and erosion. |
| 13.02 | Bushfire | |
| 13.02-1 | Bushfire planning | Bushfire planning for land affected by the Bushfire Management Overlay or included in a Bushfire Prone Area. |
| 13.03 | Floodplains | |
| 13.03-1 | Floodplain management |
|
| 13.04 | Soil degradation | |
| 13.04-1 | Contaminated and potentially contaminated land | |
| 13.04-2 | Erosion and landslip |
|
| 13.04-3 | Salinity | |
| 13.05 | Noise | |
| 13.05-1 | Noise abatement | Using building design, urban design and land separation techniques to manage noise effects on sensitive land uses. |
| 13.06 | Air quality | |
| 13.06-1 | Air quality management |
|
| 13.07 | Amenity, human health and safety | |
| 13.07-1 | Land use compatibility |
|
| 13.07-2 | Major hazard facilities |
|
| 13.07-3 | Live Music | |
| 14 | NATURAL RESOURCE MANAGEMENT | |
| 14.01 | Agriculture | |
| 14.01-1 | Protection of agricultural land |
|
| 14.01-2 | Sustainable agricultural land use |
|
| 14.01-3 | Forestry and timber production | |
| 14.02 | Water | |
| 14.02-1 | Catchment planning and management |
|
| 14.02-2 | Water quality |
|
| 14.02-3 | Protection of declared irrigation districts | |
| 14.03 | Earth and energy resources | |
| 14.03-1 | Resource exploration and extraction | |
| 15 | BUILT ENVIRONMENT AND HERITAGE | |
| 15.01 | Built environment | |
| 15.01-1 | Urban design |
|
| 15.01-2 | Building design | Building design including: residential, commercial and industrial. |
15.01-3 | Subdivision design |
|
| 15.01-4 | Healthy neighbourhoods | Designing a physical environment that supports:
|
| 15.01-5 | Neighbourhood character | |
| 15.01-6 | Design for rural areas | Design in rural areas including:
|
| 15.02 | No content | |
| 15.03 | Heritage | |
| 15.03-1 | Heritage conservation |
|
| 15.03-2 | Aboriginal cultural heritage | |
| 16 | HOUSING | |
| 16.01 | Residential development | |
| 16.01-1 | Housing supply |
|
| 16.01-2 | Housing affordability | Supporting housing affordability through:
|
| 16.01-3 | Rural residential development | Housing in areas where rural residential development is expected or preferred – excludes dwellings and dwelling lot excisions in the Farming Zone – see Clause 14.01-1 Protection of agricultural land. |
| 16.01-4 | Community care accommodation | Facilitating the confidential establishment of community care facilities. |
| 16.01-5 | Residential aged care facilities | Facilitating the development of residential aged care facilities that:
|
| 17 | ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT | |
| 17.01 | Employment | |
| 17.01-1 | Diversified economy |
|
| 17.01-2 | Innovation and research |
|
| 17.02 | Commercial | |
| 17.02-1 | Business | Meeting the community’s need for retail, entertainment, office and other commercial services. |
| 17.02-2 | Out-of-centre development | Managing out-of-centre development to not undermine existing centres and provide a net community benefit. |
| 17.03 | Industry | |
| 17.03-1 | Industrial land supply | Allocating sufficient land for all industrial needs. |
| 17.03-2 | Sustainable industry | Protecting the viability of industries through buffer distances, their location and other measures. |
| 17.03-3 | State significant industrial land | Protecting industrial land of state significance to allow for future growth. |
| 17.04 | Tourism | |
| 17.04-1 | Facilitating tourism | Excludes what is captured under Clause 17.04-2 Coastal and maritime tourism and recreation. |
| 17.04-2 | Coastal and maritime tourism and recreation | |
| 18 | TRANSPORT | |
| 18.01 | Land use and transport | |
| 18.01-1 | Land use and transport integration | Integrating land use and transport to develop a transport system that facilitates access to social, cultural, and economic activities. |
| 18.01-2 | Transport system |
|
| 18.01-3 | Sustainable and safe transport | Designing a safe transport system that promotes health and wellbeing and is sustainable. |
| 18.02 | Movement networks | |
18.02-1 | Walking |
|
| 18.02-2 | Cycling |
|
| 18.02-3 | Public Transport |
|
| 18.02-4 | Roads |
|
| 18.02-5 | Freight |
|
| 18.02-6 | Ports | |
| 18.02-7 | Airports and airfields | |
| 19 | INFRASTRUCTURE | |
| 19.01 | Energy | |
| 19.01-1 | Energy supply |
|
| 19.01-2 | Renewable energy | Renewable energy facilities on a commercial scale. |
| 19.01-3 | Pipeline infrastructure | Pipeline infrastructure provision and protection. |
| 19.02 | Community infrastructure | |
| 19.02-1 | Health facilities | Includes, hospitals, medical centres, health and health-related facilities and the like. |
| 19.02-2 | Education facilities | Includes childcare, early learning centres, kindergartens and the like. |
| 19.02-3 | Cultural facilities | Increasing access to arts, recreation and other cultural facilities. |
| 19.02-4 | Social and cultural infrastructure | Providing a fairer distribution of and access to social and cultural infrastructure, including community facilities. |
| 19.02-5 | Emergency services | Emergency service infrastructure location. |
| 19.02-6 | Open space | Public open space areas – distribution and/or management. |
| 19.03 | Development infrastructure | |
| 19.03-1 | Development and infrastructure contributions plans |
|
| 19.03-2 | Infrastructure design and provision |
|
| 19.03-3 | Integrated water management |
|
| 19.03-4 | Telecommunications |
|
| 19.03-5 | Waste and resource recovery |
|
Disclaimer
This publication may be of assistance to you but the State of Victoria and its employees do not guarantee that the publication is without flaw of any kind or is wholly appropriate for your particular purposes and therefore disclaims all liability for any error, loss or other consequence which may arise from you relying on any information in this publication.
Page last updated: 01/08/25